前言
Hybrid App(混合模式移动应用)是指介于web-app、native-app这两者之间的app,兼具“Native App良好用户交互体验的优势”和“Web App跨平台开发的优势”。

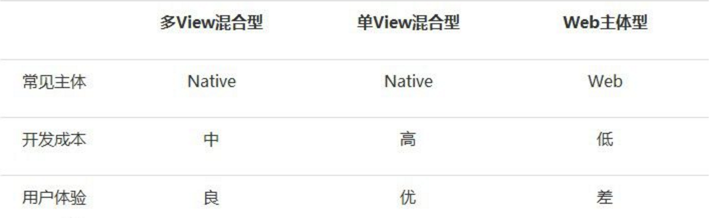
Hybrid App按网页语言与程序语言的混合,通常分为三种类型:多View混合型,单View混合型,Web主体型,3种类型比较如下:
今天我来谈谈Web主体型中Hybrid框架里面比较有名的PhoneGap
一.Cordova
说到PhoneGap,就不得不说到Cordova

Cordova 是一个可以让 JS 与原生代码(包括 Android 的 java,iOS 的 Objective-C 等)互相通信的一个库,并且提供了一系列的插件类,比如 JS 直接操作本地数据库的插件类。
Cordova的设计概念,是在APP上透过Web控件来呈现Web页面,让Web开发人员可以操作熟悉的语言、工具来开发APP.
为了让Web页面能够满足更多的APP功能需求,Cordova提供了Plugin机制,让Web页面能够挂载并调用Native开发技术所开发的功能模块
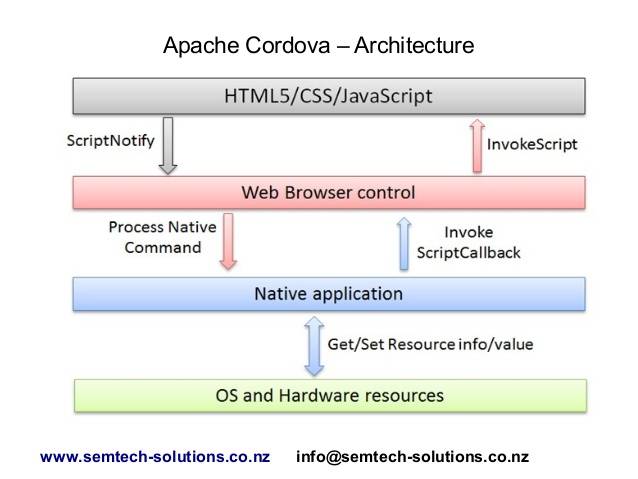
Cordova在系统中的层级应该是这样子的:

Cordova的层级结构是下图这样的:
Cordova又可以和Angular相结合,变成ngCordova
Cordova + Angular = ngCordova

二.JS 与 Objective-C 通信
JS 使用了两种方式来与 Objective-C 通信,一种是使用 XMLHttpRequest 发起请求的方式,另一种则是通过设置透明的 iframe 的 src 属性。
我接下来说的主要是第二种方式,iframe bridge。
通过在 JS 端创建一个透明的 iframe,设置这个 ifame 的 src 为自定义的协议,而 ifame 的 src 更改时,UIWebView 会先回调其 delegate 的 webView:shouldStartLoadWithRequest:navigationType: 方法
说的还是很抽象的,来实际看一段代码
在cordova.js 里面,是这样子实现的
function iOSExec() {
...
if (!isInContextOfEvalJs && commandQueue.length == 1) {
// 如果支持 XMLHttpRequest,则使用 XMLHttpRequest 方式
if (bridgeMode != jsToNativeModes.IFRAME_NAV) {
// This prevents sending an XHR when there is already one being sent.
// This should happen only in rare circumstances (refer to unit tests).
if (execXhr && execXhr.readyState != 4) {
execXhr = null;
}
// Re-using the XHR improves exec() performance by about 10%.
execXhr = execXhr || new XMLHttpRequest();
// Changing this to a GET will make the XHR reach the URIProtocol on 4.2.
// For some reason it still doesn't work though...
// Add a timestamp to the query param to prevent caching.
execXhr.open('HEAD', "/!gap_exec?" + (+new Date()), true);
if (!vcHeaderValue) {
vcHeaderValue = /.*\((.*)\)/.exec(navigator.userAgent)[1];
}
execXhr.setRequestHeader('vc', vcHeaderValue);
execXhr.setRequestHeader('rc', ++requestCount);
if (shouldBundleCommandJson()) {
// 设置请求的数据
execXhr.setRequestHeader('cmds', iOSExec.nativeFetchMessages());
}
// 发起请求
execXhr.send(null);
} else {
// 如果不支持 XMLHttpRequest,则使用透明 iframe 的方式,设置 iframe 的 src 属性
execIframe = execIframe || createExecIframe();
execIframe.src = "gap://ready";
}
}
...
}
iOS这边对应的要在WebView里面写响应的方法
// UIWebView 加载 URL 前回调的方法,返回 YES,则开始加载此 URL,返回 NO,则忽略此 URL
- (BOOL)webView:(UIWebView*)theWebView
shouldStartLoadWithRequest:(NSURLRequest*)request
navigationType:(UIWebViewNavigationType)navigationType
{
NSURL* url = [request URL];
/*
* Execute any commands queued with cordova.exec() on the JS side.
* The part of the URL after gap:// is irrelevant.
*/
// 判断是否 Cordova 的请求,对于 JS 代码中 execIframe.src = "gap://ready" 这句
if ([[url scheme] isEqualToString:@"gap"]) {
// 获取请求的数据,并对数据进行分析、处理
[_commandQueue fetchCommandsFromJs];
return NO;
}
...
}
这样就完成了JS和OC的通信了
三.Objective-C 与 JS 通信
首先OC获取JS的请求数据
- (void)fetchCommandsFromJs
{
// Grab all the queued commands from the JS side.
NSString* queuedCommandsJSON = [_viewController.webView
stringByEvaluatingJavaScriptFromString:
@"cordova.require('cordova/exec').nativeFetchMessages()"];
[self enqueCommandBatch:queuedCommandsJSON];
if ([queuedCommandsJSON length] > 0) {
CDV_EXEC_LOG(@"Exec: Retrieved new exec messages by request.");
}
}
然后OC处理JS传过来的请求
OC再把处理结果返回JS
NSString *ret = [((HFNativeFunction*)strongSelf.actionDict[funcName]) doCall:argArr];
NSString *js = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"if(typeof %@ == 'string') { paf.nativeInvocationObject=%@;} else { paf.nativeInvocationObject=JSON.stringify(%@);} ", ret, ret, ret];
DLog(@"\n\njs call fun=%@ ret=%@\n\n", funcName, ret);
[self.webView stringByEvaluatingJavaScriptFromString: js];
四.Cordova - JS工作原理
Cordova JS 端请求方法的格式:
// successCallback : 成功回调方法
// failCallback : 失败回调方法
// server : 所要请求的服务名字
// action : 所要请求的服务具体操作
// actionArgs : 请求操作所带的参数
cordova.exec(successCallback, failCallback, service, action, actionArgs);
传进来的这五个参数并不是直接传送给原生代码的,Cordova JS 端会做以下的处理:
1.会为每个请求生成一个叫 callbackId 的唯一标识:这个参数需传给 Objective-C 端,Objective-C 处理完后,会把 callbackId 连同处理结果一起返回给 JS 端。
2.以 callbackId 为 key,{success:successCallback, fail:failCallback} 为 value,把这个键值对保存在 JS 端的字典里,successCallback 与 failCallback 这两个参数不需要传给 Objective-C 端,Objective-C 返回结果时带上 callbackId,JS 端就可以根据 callbackId 找到回调方法。
3.每次 JS 请求,最后发到 Objective-C 的数据包括:callbackId, service, action, actionArgs。
JS处理请求
function iOSExec() {
...
// 生成一个 callbackId 的唯一标识,并把此标志与成功、失败回调方法一起保存在 JS 端
// Register the callbacks and add the callbackId to the positional
// arguments if given.
if (successCallback || failCallback) {
callbackId = service + cordova.callbackId++;
cordova.callbacks[callbackId] =
{success:successCallback, fail:failCallback};
}
actionArgs = massageArgsJsToNative(actionArgs);
// 把 callbackId,service,action,actionArgs 保持到 commandQueue 中
// 这四个参数就是最后发给原生代码的数据
var command = [callbackId, service, action, actionArgs];
commandQueue.push(JSON.stringify(command));
...
}
// 获取请求的数据,包括 callbackId, service, action, actionArgs
iOSExec.nativeFetchMessages = function() {
// Each entry in commandQueue is a JSON string already.
if (!commandQueue.length) {
return '';
}
var json = '[' + commandQueue.join(',') + ']';
commandQueue.length = 0;
return json;
};
五.Cordova - OC工作原理
Native OC拿到 callbackId、service、action 及 actionArgs 后,会做以下的处理:
1.根据 service 参数找到对应的插件类
2.根据 action 参数找到插件类中对应的处理方法,并把 actionArgs 作为处理方法请求参数的一部分传给处理方法
3.处理完成后,把处理结果及 callbackId 返回给 JS 端,JS 端收到后会根据 callbackId 找到回调方法,并把处理结果传给回调方法
Objective-C 返回结果给 JS 端
- (void)sendPluginResult:(CDVPluginResult*)result callbackId:(NSString*)callbackId
{
CDV_EXEC_LOG(@"Exec(%@): Sending result. Status=%@", callbackId, result.status);
// This occurs when there is are no win/fail callbacks for the call.
if ([@"INVALID" isEqualToString : callbackId]) {
return;
}
int status = [result.status intValue];
BOOL keepCallback = [result.keepCallback boolValue];
NSString* argumentsAsJSON = [result argumentsAsJSON];
// 将请求的处理结果及 callbackId 通过调用 JS 方法返回给 JS 端
NSString* js = [NSString stringWithFormat:
@"cordova.require('cordova/exec').nativeCallback('%@',%d,%@,%d)",
callbackId, status, argumentsAsJSON, keepCallback];
[self evalJsHelper:js];
}
举个具体的例子:
1.将收到的json转换成Command
// Execute the commands one-at-a-time.
NSArray* jsonEntry = [commandBatch dequeue];
if ([commandBatch count] == 0) {
[_queue removeObjectAtIndex:0];
}
HFCDVInvokedUrlCommand* command = [HFCDVInvokedUrlCommand commandFromJson:jsonEntry];
HF_CDV_EXEC_LOG(@"Exec(%@): Calling %@.%@", command.callbackId, command.className, command.methodName);
2.OC 执行
- (BOOL)execute:(HFCDVInvokedUrlCommand*)command
{
if ((command.className == nil) || (command.methodName == nil)) {
DLog(@"ERROR: Classname and/or methodName not found for command.");
return NO;
}
if ([command.className isEqualToString:@"DeviceReadyDummyClass"] &&
[command.methodName isEqualToString:@"deviceReady"]) {
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter]postNotificationName:k_NOTIF_DEVICE_READY object:_viewController];
return YES;
}
// Fetch an instance of this class
HFCDVPlugin* obj = [_viewController.commandDelegate getCommandInstance:command.className];
if (!([obj isKindOfClass:[HFCDVPlugin class]])) {
DLog(@"ERROR: Plugin '%@' not found, or is not a HFCDVPlugin. Check your plugin mapping in config.xml.", command.className);
return NO;
}
BOOL retVal = YES;
double started = [[NSDate date] timeIntervalSince1970] * 1000.0;
// Find the proper selector to call.
NSString* methodName = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@:", command.methodName];
SEL normalSelector = NSSelectorFromString(methodName);
if ([obj respondsToSelector:normalSelector]) {
// [obj performSelector:normalSelector withObject:command];
((void (*)(id, SEL, id))objc_msgSend)(obj, normalSelector, command);
} else {
// There's no method to call, so throw an error.
DLog(@"ERROR: Method '%@' not defined in Plugin '%@'", methodName, command.className);
retVal = NO;
}
double elapsed = [[NSDate date] timeIntervalSince1970] * 1000.0 - started;
if (elapsed > 10) {
DLog(@"THREAD WARNING: ['%@'] took '%f' ms. Plugin should use a background thread.", command.className, elapsed);
}
return retVal;
}
六.回调方法
JS端拿到数据根据 callbackId 回调
// 根据 callbackId 及是否成功标识,找到回调方法,并把处理结果传给回调方法
callbackFromNative: function(callbackId, success, status, args, keepCallback) {
var callback = cordova.callbacks[callbackId];
if (callback) {
if (success && status == cordova.callbackStatus.OK) {
callback.success && callback.success.apply(null, args);
} else if (!success) {
callback.fail && callback.fail.apply(null, args);
}
// Clear callback if not expecting any more results
if (!keepCallback) {
delete cordova.callbacks[callbackId];
}
}
}
GitHub Repo:Halfrost-Field
Follow: halfrost · GitHub





