前言
现在越来越多的app都使用了JSPatch实现app热修复,而JSPatch 能做到通过 JS 调用和改写 OC 方法最根本的原因是 Objective-C 是动态语言,OC 上所有方法的调用/类的生成都通过 Objective-C Runtime 在运行时进行,我们可以通过类名/方法名反射得到相应的类和方法,也可以替换某个类的方法为新的实现,理论上你可以在运行时通过类名/方法名调用到任何 OC 方法,替换任何类的实现以及新增任意类。今天就来详细解析一下OC中runtime最为吸引人的地方。
目录
- 1.objc_msgSend函数简介
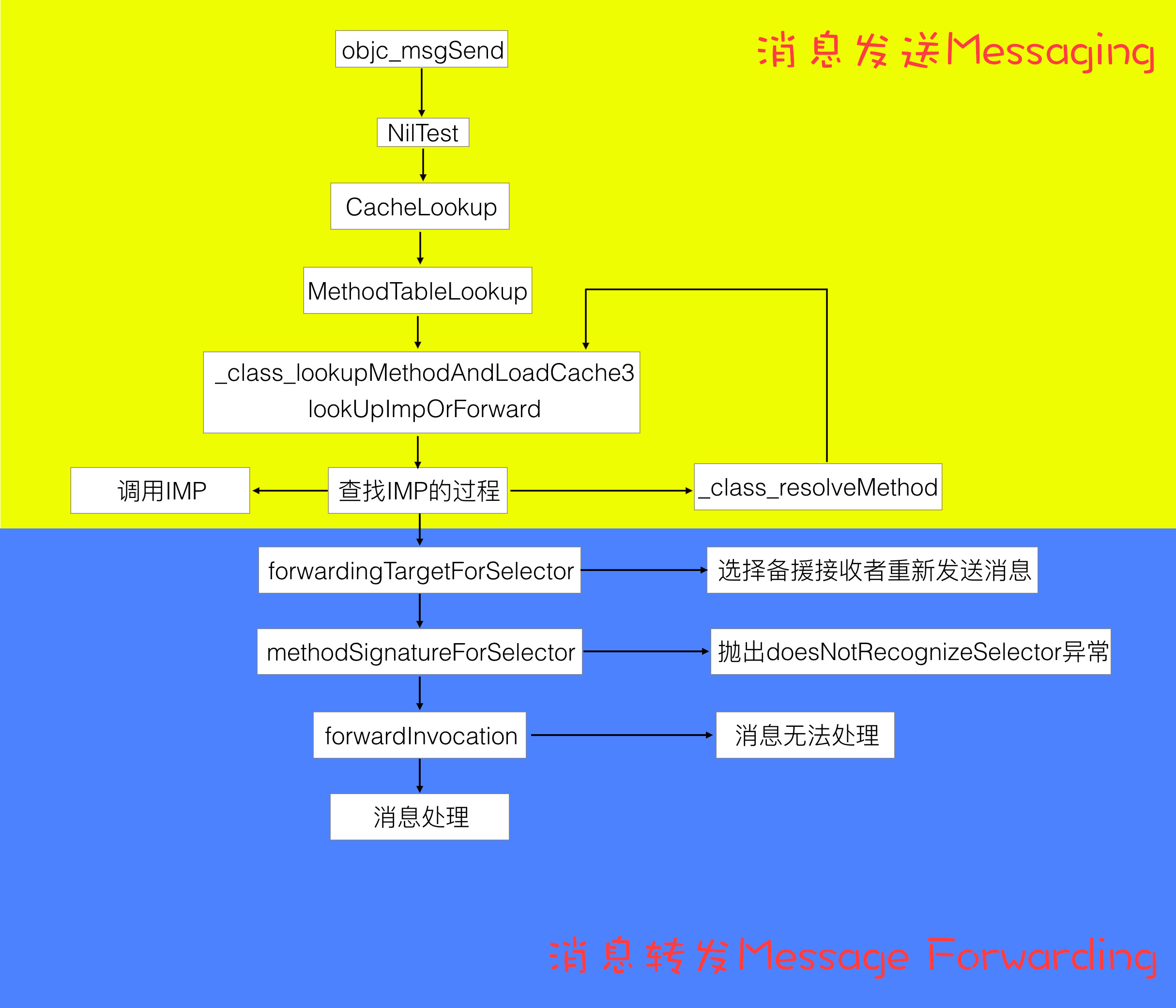
- 2.消息发送Messaging阶段—objc_msgSend源码解析
- 3.消息转发Message Forwarding阶段
- 4.forwardInvocation的例子
- 5.入院考试
- 6.Runtime中的优化
一.objc_msgSend函数简介
最初接触到OC Runtime,一定是从[receiver message]这里开始的。[receiver message]会被编译器转化为:
id objc_msgSend ( id self, SEL op, ... );
这是一个可变参数函数。第二个参数类型是SEL。SEL在OC中是selector方法选择器。
typedef struct objc_selector *SEL;
objc_selector是一个映射到方法的C字符串。需要注意的是@selector()选择子只与函数名有关。不同类中相同名字的方法所对应的方法选择器是相同的,即使方法名字相同而变量类型不同也会导致它们具有相同的方法选择器。由于这点特性,也导致了OC不支持函数重载。
在receiver拿到对应的selector之后,如果自己无法执行这个方法,那么该条消息要被转发。或者临时动态的添加方法实现。如果转发到最后依旧没法处理,程序就会崩溃。
所以编译期仅仅是确定了要发送消息,而消息如何处理是要运行期需要解决的事情。
objc_msgSend函数究竟会干什么事情呢?从这篇「objc_msgSend() Tour」文章里面可以得到一个比较详细的结论。
1. Check for ignored selectors (GC) and short-circuit.
2. Check for nil target.
If nil & nil receiver handler configured, jump to handler
If nil & no handler (default), cleanup and return.
3. Search the class’s method cache for the method IMP(use hash to find&store method in cache)
-1. If found, jump to it.
-2. Not found: lookup the method IMP in the class itself corresponding its hierarchy chain.
If found, load it into cache and jump to it.
If not found, jump to forwarding mechanism.
总结一下objc_msgSend会做一下几件事情:
1.检测这个 selector是不是要忽略的。
2.检查target是不是为nil。
如果这里有相应的nil的处理函数,就跳转到相应的函数中。
如果没有处理nil的函数,就自动清理现场并返回。这一点就是为何在OC中给nil发送消息不会崩溃的原因。
3.确定不是给nil发消息之后,在该class的缓存中查找方法对应的IMP实现。
如果找到,就跳转进去执行。
如果没有找到,就在方法分发表里面继续查找,一直找到NSObject为止。
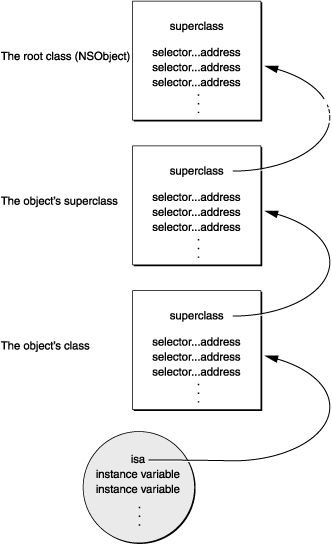
4.如果还没有找到,那就需要开始消息转发阶段了。至此,发送消息Messaging阶段完成。这一阶段主要完成的是通过select()快速查找IMP的过程。
二. 消息发送Messaging阶段—objc_msgSend源码解析
在这篇文章Obj-C Optimization: The faster objc_msgSend中看到了这样一段C版本的objc_msgSend的源码。
#include <objc/objc-runtime.h>
id c_objc_msgSend( struct objc_class /* ahem */ *self, SEL _cmd, ...)
{
struct objc_class *cls;
struct objc_cache *cache;
unsigned int hash;
struct objc_method *method;
unsigned int index;
if( self)
{
cls = self->isa;
cache = cls->cache;
hash = cache->mask;
index = (unsigned int) _cmd & hash;
do
{
method = cache->buckets[ index];
if( ! method)
goto recache;
index = (index + 1) & cache->mask;
}
while( method->method_name != _cmd);
return( (*method->method_imp)( (id) self, _cmd));
}
return( (id) self);
recache:
/* ... */
return( 0);
}
该源码中有一个do-while循环,这个循环就是上一章里面提到的在方法分发表里面查找method的过程。
不过在obj4-680里面的objc-msg-x86_64.s文件中实现是一段汇编代码。
/********************************************************************
*
* id objc_msgSend(id self, SEL _cmd,...);
*
********************************************************************/
.data
.align 3
.globl _objc_debug_taggedpointer_classes
_objc_debug_taggedpointer_classes:
.fill 16, 8, 0
ENTRY _objc_msgSend
MESSENGER_START
NilTest NORMAL
GetIsaFast NORMAL // r11 = self->isa
CacheLookup NORMAL // calls IMP on success
NilTestSupport NORMAL
GetIsaSupport NORMAL
// cache miss: go search the method lists
LCacheMiss:
// isa still in r11
MethodTableLookup %a1, %a2 // r11 = IMP
cmp %r11, %r11 // set eq (nonstret) for forwarding
jmp *%r11 // goto *imp
END_ENTRY _objc_msgSend
ENTRY _objc_msgSend_fixup
int3
END_ENTRY _objc_msgSend_fixup
STATIC_ENTRY _objc_msgSend_fixedup
// Load _cmd from the message_ref
movq 8(%a2), %a2
jmp _objc_msgSend
END_ENTRY _objc_msgSend_fixedup
来分析一下这段汇编代码。
乍一看,如果从LCacheMiss:这里上下分开,可以很明显的看到objc_msgSend就干了两件事情—— CacheLookup 和 MethodTableLookup。
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// NilTest return-type
//
// Takes: $0 = NORMAL or FPRET or FP2RET or STRET
// %a1 or %a2 (STRET) = receiver
//
// On exit: Loads non-nil receiver in %a1 or %a2 (STRET), or returns zero.
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
.macro NilTest
.if $0 == SUPER || $0 == SUPER_STRET
error super dispatch does not test for nil
.endif
.if $0 != STRET
testq %a1, %a1
.else
testq %a2, %a2
.endif
PN
jz LNilTestSlow_f
.endmacro
NilTest是用来检测是否为nil的。传入参数有4种,NORMAL / FPRET / FP2RET / STRET。
objc_msgSend 传入的参数是NilTest NORMAL
objc_msgSend_fpret 传入的参数是NilTest FPRET
objc_msgSend_fp2ret 传入的参数是NilTest FP2RET
objc_msgSend_stret 传入的参数是NilTest STRET
如果检测方法的接受者是nil,那么系统会自动clean并且return。
GetIsaFast宏可以快速地获取到对象的 isa 指针地址(放到 r11 寄存器,r10会被重写;在 arm 架构上是直接赋值到 r9)
.macro CacheLookup
ldrh r12, [r9, #CACHE_MASK] // r12 = mask
ldr r9, [r9, #CACHE] // r9 = buckets
.if $0 == STRET || $0 == SUPER_STRET
and r12, r12, r2 // r12 = index = SEL & mask
.else
and r12, r12, r1 // r12 = index = SEL & mask
.endif
add r9, r9, r12, LSL #3 // r9 = bucket = buckets+index*8
ldr r12, [r9] // r12 = bucket->sel
2:
.if $0 == STRET || $0 == SUPER_STRET
teq r12, r2
.else
teq r12, r1
.endif
bne 1f
CacheHit $0
1:
cmp r12, #1
blo LCacheMiss_f // if (bucket->sel == 0) cache miss
it eq // if (bucket->sel == 1) cache wrap
ldreq r9, [r9, #4] // bucket->imp is before first bucket
ldr r12, [r9, #8]! // r12 = (++bucket)->sel
b 2b
.endmacro
r12里面存的是方法method,r9里面是cache。r1,r2是SEL。在这个CacheLookup函数中,不断的通过SEL与cache中的bucket->sel进行比较,如果r12 = = 0,则跳转到LCacheMiss_f标记去继续执行。如果r12找到了,r12 = =1,即在cache中找到了相应的SEL,则直接执行该IMP(放在r10中)。
程序跳到LCacheMiss,就说明cache中无缓存,未命中缓存。这个时候就要开始下一阶段MethodTableLookup的查找了。
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// MethodTableLookup classRegister, selectorRegister
//
// Takes: $0 = class to search (a1 or a2 or r10 ONLY)
// $1 = selector to search for (a2 or a3 ONLY)
// r11 = class to search
//
// On exit: imp in %r11
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
.macro MethodTableLookup
MESSENGER_END_SLOW
SaveRegisters
// _class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3(receiver, selector, class)
movq $0, %a1
movq $1, %a2
movq %r11, %a3
call __class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3
// IMP is now in %rax
movq %rax, %r11
RestoreRegisters
.endmacro
MethodTableLookup 可以算是个接口层宏,主要用于保存环境与准备参数,来调用 __class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3函数(在objc-class.mm中)。具体是把receiver, selector, class三个参数传给$0,$1,r11,然后再去调用lookupMethodAndLoadCache3方法。最后会将 IMP 返回(从 r11 挪到 rax)。最后在 objc_msgSend中调用 IMP。
/***********************************************************************
* _class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache.
* Method lookup for dispatchers ONLY. OTHER CODE SHOULD USE lookUpImp().
* This lookup avoids optimistic cache scan because the dispatcher
* already tried that.
**********************************************************************/
IMP _class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3(id obj, SEL sel, Class cls)
{
return lookUpImpOrForward(cls, sel, obj,
YES/*initialize*/, NO/*cache*/, YES/*resolver*/);
}
__class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3函数也是个接口层(C编写),此函数提供相应参数配置,实际功能在lookUpImpOrForward函数中。
再来看看lookUpImpOrForward函数实现
IMP lookUpImpOrForward(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst,
bool initialize, bool cache, bool resolver)
{
Class curClass;
IMP imp = nil;
Method meth;
bool triedResolver = NO;
/*
中间是查找过程,详细解析见下。
*/
// paranoia: look for ignored selectors with non-ignored implementations
assert(!(ignoreSelector(sel) && imp != (IMP)&_objc_ignored_method));
// paranoia: never let uncached leak out
assert(imp != _objc_msgSend_uncached_impcache);
return imp;
}
接下来一行行的解析。
runtimeLock.assertUnlocked();
runtimeLock.assertUnlocked(); 这个是加一个读写锁,保证线程安全。
// Optimistic cache lookup
if (cache) {
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp) return imp;
}
lookUpImpOrForward第5个新参是是否找到cache的布尔量,如果传入的是YES,那么就会调用cache_getImp方法去找到缓存里面的IMP。
/********************************************************************
* IMP cache_getImp(Class cls, SEL sel)
*
* On entry: a1 = class whose cache is to be searched
* a2 = selector to search for
*
* If found, returns method implementation.
* If not found, returns NULL.
********************************************************************/
STATIC_ENTRY _cache_getImp
// do lookup
movq %a1, %r11 // move class to r11 for CacheLookup
CacheLookup GETIMP // returns IMP on success
LCacheMiss:
// cache miss, return nil
xorl %eax, %eax
ret
LGetImpExit:
END_ENTRY _cache_getImp
cache_getImp会把找到的IMP放在r11中。
if (!cls->isRealized()) {
rwlock_writer_t lock(runtimeLock);
realizeClass(cls);
}
调用realizeClass方法是申请class_rw_t的可读写空间。
if (initialize && !cls->isInitialized()) {
_class_initialize (_class_getNonMetaClass(cls, inst));
}
_class_initialize是类初始化的过程。
retry:
runtimeLock.read();
runtimeLock.read();这里加了一个读锁。因为在运行时中会动态的添加方法,为了保证线程安全,所以要加锁。从这里开始,下面会出现5处goto done的地方,和一处goto retry。
done:
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
在done的地方,会完成IMP的查找,于是可以打开读锁。
// Ignore GC selectors
if (ignoreSelector(sel)) {
imp = _objc_ignored_method;
cache_fill(cls, sel, imp, inst);
goto done;
}
紧接着GC selectors是为了忽略macOS中GC垃圾回收机制用到的方法,iOS则没有这一步。如果忽略,则进行cache_fill,然后跳转到goto done那里去。
void cache_fill(Class cls, SEL sel, IMP imp, id receiver)
{
#if !DEBUG_TASK_THREADS
mutex_locker_t lock(cacheUpdateLock);
cache_fill_nolock(cls, sel, imp, receiver);
#else
_collecting_in_critical();
return;
#endif
}
static void cache_fill_nolock(Class cls, SEL sel, IMP imp, id receiver)
{
cacheUpdateLock.assertLocked();
// Never cache before +initialize is done
if (!cls->isInitialized()) return;
// Make sure the entry wasn't added to the cache by some other thread
// before we grabbed the cacheUpdateLock.
if (cache_getImp(cls, sel)) return;
cache_t *cache = getCache(cls);
cache_key_t key = getKey(sel);
// Use the cache as-is if it is less than 3/4 full
mask_t newOccupied = cache->occupied() + 1;
mask_t capacity = cache->capacity();
if (cache->isConstantEmptyCache()) {
// Cache is read-only. Replace it.
cache->reallocate(capacity, capacity ?: INIT_CACHE_SIZE);
}
else if (newOccupied <= capacity / 4 * 3) {
// Cache is less than 3/4 full. Use it as-is.
}
else {
// Cache is too full. Expand it.
cache->expand();
}
bucket_t *bucket = cache->find(key, receiver);
if (bucket->key() == 0) cache->incrementOccupied();
bucket->set(key, imp);
}
在cache_fill中还会去调用cache_fill_nolock函数,如果缓存中的内容大于容量的 3/4就会扩充缓存,使缓存的大小翻倍。找到第一个空的 bucket_t,以 (SEL, IMP)的形式填充进去。
// Try this class's cache.
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp) goto done;
如果不忽略,则再次尝试从类的cache中获取IMP,如果获取到,然后也会跳转到goto done去。
// Try this class's method lists.
meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(cls, sel);
if (meth) {
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, cls);
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
如果在cache缓存中获取失败,则再去类方法列表里面进行查找。找到后跳转到goto done。
// Try superclass caches and method lists.
curClass = cls;
while ((curClass = curClass->superclass)) {
// Superclass cache.
imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel);
if (imp) {
if (imp != (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache) {
// Found the method in a superclass. Cache it in this class.
log_and_fill_cache(cls, imp, sel, inst, curClass);
goto done;
}
else {
// Found a forward:: entry in a superclass.
// Stop searching, but don't cache yet; call method
// resolver for this class first.
break;
}
}
如果以上尝试都失败了,接下来就会循环尝试父类的缓存和方法列表。一直找到NSObject为止。因为NSObject的superclass为nil,才跳出循环。
如果在父类中找到了该方法method的IMP,接下来就应该把这个方法cache回自己的缓存中。fill完之后跳转goto done语句。
// Superclass method list.
meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(curClass, sel);
if (meth) {
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, curClass);
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
}
如果没有在父类的cache中找到IMP,继续在父类的方法列表里面查找。如果找到,跳转goto done语句。
static method_t * getMethodNoSuper_nolock(Class cls, SEL sel)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
assert(cls->isRealized());
// fixme nil cls?
// fixme nil sel?
for (auto mlists = cls->data()->methods.beginLists(),
end = cls->data()->methods.endLists();
mlists != end;
++mlists)
{
method_t *m = search_method_list(*mlists, sel);
if (m) return m;
}
return nil;
}
这里可以解析一下method的查找过程。在getMethodNoSuper_nolock方法中,会遍历一次methodList链表,从begin一直遍历到end。遍历过程中会调用search_method_list函数。
static method_t *search_method_list(const method_list_t *mlist, SEL sel)
{
int methodListIsFixedUp = mlist->isFixedUp();
int methodListHasExpectedSize = mlist->entsize() == sizeof(method_t);
if (__builtin_expect(methodListIsFixedUp && methodListHasExpectedSize, 1)) {
return findMethodInSortedMethodList(sel, mlist);
} else {
// Linear search of unsorted method list
for (auto& meth : *mlist) {
if (meth.name == sel) return &meth;
}
}
#if DEBUG
// sanity-check negative results
if (mlist->isFixedUp()) {
for (auto& meth : *mlist) {
if (meth.name == sel) {
_objc_fatal("linear search worked when binary search did not");
}
}
}
#endif
return nil;
}
在search_method_list函数中,会去判断当前methodList是否有序,如果有序,会调用findMethodInSortedMethodList方法,这个方法里面的实现是一个二分搜索,具体代码就不贴了。如果非有序,就调用线性的傻瓜式遍历搜索。
// No implementation found. Try method resolver once.
if (resolver && !triedResolver) {
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
_class_resolveMethod(cls, sel, inst);
// Don't cache the result; we don't hold the lock so it may have
// changed already. Re-do the search from scratch instead.
triedResolver = YES;
goto retry;
}
如果父类找到NSObject还没有找到,那么就会开始尝试_class_resolveMethod方法。注意,这些需要打开读锁,因为开发者可能会在这里动态增加方法实现,所以不需要缓存结果。此处虽然锁被打开,可能会出现线程问题,所以在执行完_class_resolveMethod方法之后,会goto retry,重新执行一遍之前查找的过程。
/***********************************************************************
* _class_resolveMethod
* Call +resolveClassMethod or +resolveInstanceMethod.
* Returns nothing; any result would be potentially out-of-date already.
* Does not check if the method already exists.
**********************************************************************/
void _class_resolveMethod(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst)
{
if (! cls->isMetaClass()) {
// try [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
_class_resolveInstanceMethod(cls, sel, inst);
}
else {
// try [nonMetaClass resolveClassMethod:sel]
// and [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
_class_resolveClassMethod(cls, sel, inst);
if (!lookUpImpOrNil(cls, sel, inst,
NO/*initialize*/, YES/*cache*/, NO/*resolver*/))
{
_class_resolveInstanceMethod(cls, sel, inst);
}
}
}
这个函数首先判断是否是meta-class类,如果不是元类,就执行_class_resolveInstanceMethod,如果是元类,执行_class_resolveClassMethod。这里有一个lookUpImpOrNil的函数调用。
IMP lookUpImpOrNil(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst,
bool initialize, bool cache, bool resolver)
{
IMP imp = lookUpImpOrForward(cls, sel, inst, initialize, cache, resolver);
if (imp == _objc_msgForward_impcache) return nil;
else return imp;
}
在这个函数实现中,还会去调用lookUpImpOrForward去查找有没有传入的sel的实现,但是返回值还会返回nil。在imp == _objc_msgForward_impcache会返回nil。_objc_msgForward_impcache是一个标记,这个标记用来表示在父类的缓存中停止继续查找。
IMP class_getMethodImplementation(Class cls, SEL sel)
{
IMP imp;
if (!cls || !sel) return nil;
imp = lookUpImpOrNil(cls, sel, nil,
YES/*initialize*/, YES/*cache*/, YES/*resolver*/);
// Translate forwarding function to C-callable external version
if (!imp) {
return _objc_msgForward;
}
return imp;
}
再回到_class_resolveMethod的实现中,如果lookUpImpOrNil返回nil,就代表在父类中的缓存中找到,于是需要再调用一次_class_resolveInstanceMethod方法。保证给sel添加上了对应的IMP。
// No implementation found, and method resolver didn't help.
// Use forwarding.
imp = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache;
cache_fill(cls, sel, imp, inst);
回到lookUpImpOrForward方法中,如果也没有找到IMP的实现,那么method resolver也没用了,只能进入消息转发阶段。进入这个阶段之前,imp变成_objc_msgForward_impcache。最后再加入缓存中。
三. 消息转发Message Forwarding阶段
到了转发阶段,会调用id _objc_msgForward(id self, SEL _cmd,...)方法。在objc-msg-x86_64.s中有其汇编的实现。
STATIC_ENTRY __objc_msgForward_impcache
// Method cache version
// THIS IS NOT A CALLABLE C FUNCTION
// Out-of-band condition register is NE for stret, EQ otherwise.
MESSENGER_START
nop
MESSENGER_END_SLOW
jne __objc_msgForward_stret
jmp __objc_msgForward
END_ENTRY __objc_msgForward_impcache
ENTRY __objc_msgForward
// Non-stret version
movq __objc_forward_handler(%rip), %r11
jmp *%r11
END_ENTRY __objc_msgForward
在执行_objc_msgForward之后会调用__objc_forward_handler函数。
// Default forward handler halts the process.
__attribute__((noreturn)) void objc_defaultForwardHandler(id self, SEL sel)
{
_objc_fatal("%c[%s %s]: unrecognized selector sent to instance %p "
"(no message forward handler is installed)",
class_isMetaClass(object_getClass(self)) ? '+' : '-',
object_getClassName(self), sel_getName(sel), self);
}
在最新的Objc2.0中会有一个objc_defaultForwardHandler,看源码实现我们可以看到熟悉的语句。当我们给一个对象发送一个没有实现的方法的时候,如果其父类也没有这个方法,则会崩溃,报错信息类似于这样:unrecognized selector sent to instance,然后接着会跳出一些堆栈信息。这些信息就是从这里而来。
void *_objc_forward_handler = (void*)objc_defaultForwardHandler;
#if SUPPORT_STRET
struct stret { int i[100]; };
__attribute__((noreturn)) struct stret objc_defaultForwardStretHandler(id self, SEL sel)
{
objc_defaultForwardHandler(self, sel);
}
void *_objc_forward_stret_handler = (void*)objc_defaultForwardStretHandler;
#endif
#endif
void objc_setForwardHandler(void *fwd, void *fwd_stret)
{
_objc_forward_handler = fwd;
#if SUPPORT_STRET
_objc_forward_stret_handler = fwd_stret;
#endif
}
要设置转发只要重写_objc_forward_handler方法即可。在objc_setForwardHandler方法中,可以设置ForwardHandler。
但是当你想要弄清objc_setForwardHandler调用栈的情况的时候,你会发现打印不出来入口。因为苹果在这里做了点手脚。关于objc_setForwardHandler的调用,以及之后的消息转发调用栈的问题,需要用到逆向的知识。推荐大家看这两篇文章就会明白其中的原理。
Objective-C 消息发送与转发机制原理
Hmmm, What’s that Selector?
还是回到消息转发上面来。当前的SEL无法找到相应的IMP的时候,开发者可以通过重写- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector方法来“偷梁换柱”,把消息的接受者换成一个可以处理该消息的对象。
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector
{
if(aSelector == @selector(Method:)){
return otherObject;
}
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}
当然也可以替换类方法,那就要重写 + (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector方法,返回值是一个类对象。
+ (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
if(aSelector == @selector(xxx)) {
return NSClassFromString(@"Class name");
}
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}
这一步是替消息找备援接收者,如果这一步返回的是nil,那么补救措施就完全的失效了,Runtime系统会向对象发送methodSignatureForSelector:消息,并取到返回的方法签名用于生成NSInvocation对象。为接下来的完整的消息转发生成一个 NSMethodSignature对象。NSMethodSignature 对象会被包装成 NSInvocation 对象,forwardInvocation: 方法里就可以对 NSInvocation 进行处理了。
接下来未识别的方法崩溃之前,系统会做一次完整的消息转发。
我们只需要重写下面这个方法,就可以自定义我们自己的转发逻辑了。
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation
{
if ([someOtherObject respondsToSelector:
[anInvocation selector]])
[anInvocation invokeWithTarget:someOtherObject];
else
[super forwardInvocation:anInvocation];
}
实现此方法之后,若发现某调用不应由本类处理,则会调用超类的同名方法。如此,继承体系中的每个类都有机会处理该方法调用的请求,一直到NSObject根类。如果到NSObject也不能处理该条消息,那么就是再无挽救措施了,只能抛出“doesNotRecognizeSelector”异常了。
至此,消息发送和转发的过程都清楚明白了。
四. forwardInvocation的例子

这里我想举一个好玩的例子,来说明一下forwardInvocation的使用方法。
这个例子中我们会利用runtime消息转发机制创建一个动态代理。利用这个动态代理来转发消息。这里我们会用到两个基类的另外一个神秘的类,NSProxy。
NSProxy类和NSObject同为OC里面的基类,但是NSProxy类是一种抽象的基类,无法直接实例化,可用于实现代理模式。它通过实现一组经过简化的方法,代替目标对象捕捉和处理所有的消息。NSProxy类也同样实现了NSObject的协议声明的方法,而且它有两个必须实现的方法。
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)invocation;
- (nullable NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)sel NS_SWIFT_UNAVAILABLE("NSInvocation and related APIs not available");
另外还需要说明的是,NSProxy类的子类必须声明并实现至少一个init方法,这样才能符合OC中创建和初始化对象的惯例。Foundation框架里面也含有多个NSProxy类的具体实现类。
- NSDistantObject类:定义其他应用程序或线程中对象的代理类。
- NSProtocolChecker类:定义对象,使用这话对象可以限定哪些消息能够发送给另外一个对象。
接下来就来看看下面这个好玩的例子。
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface Student : NSObject
-(void)study:(NSString *)subject andRead:(NSString *)bookName;
-(void)study:(NSString *)subject :(NSString *)bookName;
@end
定义一个student类,里面随便给两个方法。
#import "Student.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h>
@implementation Student
-(void)study:(NSString *)subject :(NSString *)bookName
{
NSLog(@"Invorking method on %@ object with selector %@",[self class],NSStringFromSelector(_cmd));
}
-(void)study:(NSString *)subject andRead:(NSString *)bookName
{
NSLog(@"Invorking method on %@ object with selector %@",[self class],NSStringFromSelector(_cmd));
}
@end
在两个方法实现里面增加log信息,这是为了一会打印的时候方便知道调用了哪个方法。
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import "Invoker.h"
@interface AspectProxy : NSProxy
/** 通过NSProxy实例转发消息的真正对象 */
@property(strong) id proxyTarget;
/** 能够实现横切功能的类(遵守Invoker协议)的实例 */
@property(strong) id<Invoker> invoker;
/** 定义了哪些消息会调用横切功能 */
@property(readonly) NSMutableArray *selectors;
// AspectProxy类实例的初始化方法
- (id)initWithObject:(id)object andInvoker:(id<Invoker>)invoker;
- (id)initWithObject:(id)object selectors:(NSArray *)selectors andInvoker:(id<Invoker>)invoker;
// 向当前的选择器列表中添加选择器
- (void)registerSelector:(SEL)selector;
@end
定义一个AspectProxy类,这个类专门用来转发消息的。
#import "AspectProxy.h"
@implementation AspectProxy
- (id)initWithObject:(id)object selectors:(NSArray *)selectors andInvoker:(id<Invoker>)invoker{
_proxyTarget = object;
_invoker = invoker;
_selectors = [selectors mutableCopy];
return self;
}
- (id)initWithObject:(id)object andInvoker:(id<Invoker>)invoker{
return [self initWithObject:object selectors:nil andInvoker:invoker];
}
// 添加另外一个选择器
- (void)registerSelector:(SEL)selector{
NSValue *selValue = [NSValue valueWithPointer:selector];
[self.selectors addObject:selValue];
}
// 为目标对象中被调用的方法返回一个NSMethodSignature实例
// 运行时系统要求在执行标准转发时实现这个方法
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)sel{
return [self.proxyTarget methodSignatureForSelector:sel];
}
/**
* 当调用目标方法的选择器与在AspectProxy对象中注册的选择器匹配时,forwardInvocation:会
* 调用目标对象中的方法,并根据条件语句的判断结果调用AOP(面向切面编程)功能
*/
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)invocation{
// 在调用目标方法前执行横切功能
if ([self.invoker respondsToSelector:@selector(preInvoke:withTarget:)]) {
if (self.selectors != nil) {
SEL methodSel = [invocation selector];
for (NSValue *selValue in self.selectors) {
if (methodSel == [selValue pointerValue]) {
[[self invoker] preInvoke:invocation withTarget:self.proxyTarget];
break;
}
}
}else{
[[self invoker] preInvoke:invocation withTarget:self.proxyTarget];
}
}
// 调用目标方法
[invocation invokeWithTarget:self.proxyTarget];
// 在调用目标方法后执行横切功能
if ([self.invoker respondsToSelector:@selector(postInvoke:withTarget:)]) {
if (self.selectors != nil) {
SEL methodSel = [invocation selector];
for (NSValue *selValue in self.selectors) {
if (methodSel == [selValue pointerValue]) {
[[self invoker] postInvoke:invocation withTarget:self.proxyTarget];
break;
}
}
}else{
[[self invoker] postInvoke:invocation withTarget:self.proxyTarget];
}
}
}
接着我们定义一个代理协议
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@protocol Invoker <NSObject>
@required
// 在调用对象中的方法前执行对功能的横切
- (void)preInvoke:(NSInvocation *)inv withTarget:(id)target;
@optional
// 在调用对象中的方法后执行对功能的横切
- (void)postInvoke:(NSInvocation *)inv withTarget:(id)target;
@end
最后还需要一个遵守协议的类
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import "Invoker.h"
@interface AuditingInvoker : NSObject<Invoker>//遵守Invoker协议
@end
#import "AuditingInvoker.h"
@implementation AuditingInvoker
- (void)preInvoke:(NSInvocation *)inv withTarget:(id)target{
NSLog(@"before sending message with selector %@ to %@ object", NSStringFromSelector([inv selector]),[target className]);
}
- (void)postInvoke:(NSInvocation *)inv withTarget:(id)target{
NSLog(@"after sending message with selector %@ to %@ object", NSStringFromSelector([inv selector]),[target className]);
}
@end
在这个遵循代理类里面我们只实现协议里面的两个方法。
写出测试代码
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import "AspectProxy.h"
#import "AuditingInvoker.h"
#import "Student.h"
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
id student = [[Student alloc] init];
// 设置代理中注册的选择器数组
NSValue *selValue1 = [NSValue valueWithPointer:@selector(study:andRead:)];
NSArray *selValues = @[selValue1];
// 创建AuditingInvoker
AuditingInvoker *invoker = [[AuditingInvoker alloc] init];
// 创建Student对象的代理studentProxy
id studentProxy = [[AspectProxy alloc] initWithObject:student selectors:selValues andInvoker:invoker];
// 使用指定的选择器向该代理发送消息---例子1
[studentProxy study:@"Computer" andRead:@"Algorithm"];
// 使用还未注册到代理中的其他选择器,向这个代理发送消息!---例子2
[studentProxy study:@"mathematics" :@"higher mathematics"];
// 为这个代理注册一个选择器并再次向其发送消息---例子3
[studentProxy registerSelector:@selector(study::)];
[studentProxy study:@"mathematics" :@"higher mathematics"];
}
return 0;
}
这里有3个例子。里面会分别输出什么呢?
before sending message with selector study:andRead: to Student object
Invorking method on Student object with selector study:andRead:
after sending message with selector study:andRead: to Student object
Invorking method on Student object with selector study::
before sending message with selector study:: to Student object
Invorking method on Student object with selector study::
after sending message with selector study:: to Student object
例子1中会输出3句话。调用Student对象的代理中的study:andRead:方法,会使该代理调用AuditingInvoker对象中的preInvoker:方法、真正目标(Student对象)中的study:andRead:方法,以及AuditingInvoker对象中的postInvoker:方法。一个方法的调用,调用起了3个方法。原因是study:andRead:方法是通过Student对象的代理注册的;
例子2就只会输出1句话。调用Student对象代理中的study::方法,因为该方法还未通过这个代理注册,所以程序仅会将调用该方法的消息转发给Student对象,而不会调用AuditorInvoker方法。
例子3又会输出3句话了。因为study::通过这个代理进行了注册,然后程序再次调用它,在这次调用过程中,程序会调用AuditingInvoker对象中的AOP方法和真正目标(Student对象)中的study::方法。
这个例子就实现了一个简单的AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)面向切面编程。我们把一切功能"切"出去,与其他部分分开,这样可以提高程序的模块化程度。AOP能解耦也能动态组装,可以通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现在不修改源代码的情况下给程序动态统一添加功能。比如上面的例子三,我们通过把方法注册到动态代理类中,于是就实现了该类也能处理方法的功能。
五. 入院考试

下面的代码会?Compile Error / Runtime Crash / NSLog…?
@interface NSObject (Sark)
+ (void)foo;
- (void)foo;
@end
@implementation NSObject (Sark)
- (void)foo
{
NSLog(@"IMP: -[NSObject(Sark) foo]");
}
@end
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
[NSObject foo];
[[NSObject new] foo];
}
return 0;
}
这道有两处难点,难点一是给NSObject增加了一个分类,分类声明的是一个加号的类方法,而实现中是一个减号的实例方法。在main中去NSObject去调用了这个foo方法,会编译错误,还是会Crash呢?
难点二是会输出什么内容呢?
先来看难点一,这里会牵扯到Category的知识。推荐文章还是美团的这篇经典的深入理解Objective-C:Category
void _objc_init(void)
{
static bool initialized = false;
if (initialized) return;
initialized = true;
// fixme defer initialization until an objc-using image is found?
environ_init();
tls_init();
lock_init();
exception_init();
// Register for unmap first, in case some +load unmaps something
_dyld_register_func_for_remove_image(&unmap_image);
dyld_register_image_state_change_handler(dyld_image_state_bound,
1/*batch*/, &map_images);
dyld_register_image_state_change_handler(dyld_image_state_dependents_initialized, 0/*not batch*/, &load_images);
}
OC在初始化的时候,会去加载map_images,map_images最终会调用objc-runtime-new.mm里面的_read_images方法。_read_images方法里面会去初始化内存中的map, 这个时候将会load所有的类,协议还有Category。NSOBject的+load方法就是这个时候调用的。
// Discover categories.
for (EACH_HEADER) {
category_t **catlist =
_getObjc2CategoryList(hi, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
category_t *cat = catlist[i];
class_t *cls = remapClass(cat->cls);
if (!cls) {
// Category's target class is missing (probably weak-linked).
// Disavow any knowledge of this category.
catlist[i] = NULL;
if (PrintConnecting) {
_objc_inform("CLASS: IGNORING category \?\?\?(%s) %p with "
"missing weak-linked target class",
cat->name, cat);
}
continue;
}
// Process this category.
// First, register the category with its target class.
// Then, rebuild the class's method lists (etc) if
// the class is realized.
BOOL classExists = NO;
if (cat->instanceMethods || cat->protocols
|| cat->instanceProperties)
{
addUnattachedCategoryForClass(cat, cls, hi);
if (isRealized(cls)) {
remethodizeClass(cls);
classExists = YES;
}
if (PrintConnecting) {
_objc_inform("CLASS: found category -%s(%s) %s",
getName(cls), cat->name,
classExists ? "on existing class" : "");
}
}
if (cat->classMethods || cat->protocols
/* || cat->classProperties */)
{
addUnattachedCategoryForClass(cat, cls->isa, hi);
if (isRealized(cls->isa)) {
remethodizeClass(cls->isa);
}
if (PrintConnecting) {
_objc_inform("CLASS: found category +%s(%s)",
getName(cls), cat->name);
}
}
}
}
在这个加载中,for循环中会反复调用_getObjc2CategoryList
方法,这个方法的具体实现是:
// function name content type section name
GETSECT(_getObjc2CategoryList, category_t *, "__objc_catlist");
最后一个参数__objc_catlist就是编译器刚刚生成的category数组。
加载完所有的category之后,就开始处理这些类别。大体思路还是分为2类来分开处理。
if (cat->instanceMethods || cat->protocols || cat->instanceProperties){
}
第一类是实例方法
if (cat->classMethods || cat->protocols /* || cat->classProperties */) {
}
第二类是类方法。
处理完之后的结果
1)、把category的实例方法、协议以及属性添加到类上
2)、把category的类方法和协议添加到类的metaclass上
这两种情况里面的处理方式都差不多,先去调用addUnattachedCategoryForClass函数,申请内存,分配空间。remethodizeClass这个方法里面会调用attachCategories方法。
attachCategories方法代码就不贴了,有兴趣的可以自己去看看。这个方法里面会用头插法,把新加的方法从头插入方法链表中。并且最后还会flushCaches。
这也就是为什么我们可以在Category里面覆盖原有的方法的原因,因为头插法,新的方法在链表的前面,会优先被遍历到。
以上就是Category加载时候的流程。
再回到这道题目上面来,在加载NSObject的Category中,在编译期会提示我们没有实现+(void)foo的方法,因为在.m文件中并没有找到+的方法,而是一个-号的方法,所以会提示。
但是在实际加载Category的时候,会把-(void)foo加载进去,由于是实例方法,所以会放在NSObject的实例方法链表里面。
根据第二章分析的objc_msgSend源码实现,我们可以知道:
在调用[NSObject foo]的时候,会先在NSObject的meta-class中去查找foo方法的IMP,未找到,继续在superClass中去查找,NSObject的meta-class的superClass就是本身NSObject,于是又回到NSObject的类方法中查找foo方法,于是乎找到了,执行foo方法,输出
IMP: -[NSObject(Sark) foo]
在调用[[NSObject new] foo]的时候,会先生成一个NSObject的对象,用这个NSObject实例对象再去调用foo方法的时候,会去NSObject的类方法里面去查找,找到,于是也会输出
IMP: -[NSObject(Sark) foo]
所以上面这题,不会Compile Error ,更不会 Runtime Crash ,会输出两个相同的结果。
六. Runtime中的优化

关于Runtime系统中,有3种地方进行了优化。
- 1.方法列表的缓存
- 2.虚函数表vTable
- 3.dyld共享缓存
1.方法列表的缓存
在消息发送过程中,查找IMP的过程,会优先查找缓存。这个缓存会存储最近使用过的方法都缓存起来。这个cache和CPU里面的cache的工作方式有点类似。原理是调用的方法有可能经常会被调用。如果没有这个缓存,直接去类方法的方法链表里面去查找,查询效率实在太低。所以查找IMP会优先搜索饭方法缓存,如果没有找到,接着会在虚函数表中寻找IMP。如果找到了,就会把这个IMP存储到缓存中备用。
基于这个设计,使Runtime系统能能够执行快速高效的方法查询操作。
2.虚函数表
虚函数表也称为分派表,是编程语言中常用的动态绑定支持机制。在OC的Runtime运行时系统库实现了一种自定义的虚函数表分派机制。这个表是专门用来提高性能和灵活性的。这个虚函数表是用来存储IMP类型的数组。每个object-class都有这样一个指向虚函数表的指针。
3.dyld共享缓存
在我们的程序中,一定会有很多自定义类,而这些类中,很多SEL是重名的,比如alloc,init等等。Runtime系统需要为每一个方法给定一个SEL指针,然后为每次调用个各个方法更新元数据,以获取唯一值。这个过程是在应用程序启动的时候完成。为了提高这一部分的执行效率,Runtime会通过dyld共享缓存实现选择器的唯一性。
dyld是一种系统服务,用于定位和加载动态库。它含有共享缓存,能够使多个进程共用这些动态库。dyld共享缓存中含有一个选择器表,从而能使运行时系统能够通过使用缓存访问共享库和自定义类的选择器。
关于dyld的知识可以看看这篇文章dyld: Dynamic Linking On OS X
未完待续,请大家多多指教。